Frequently Asked Questions
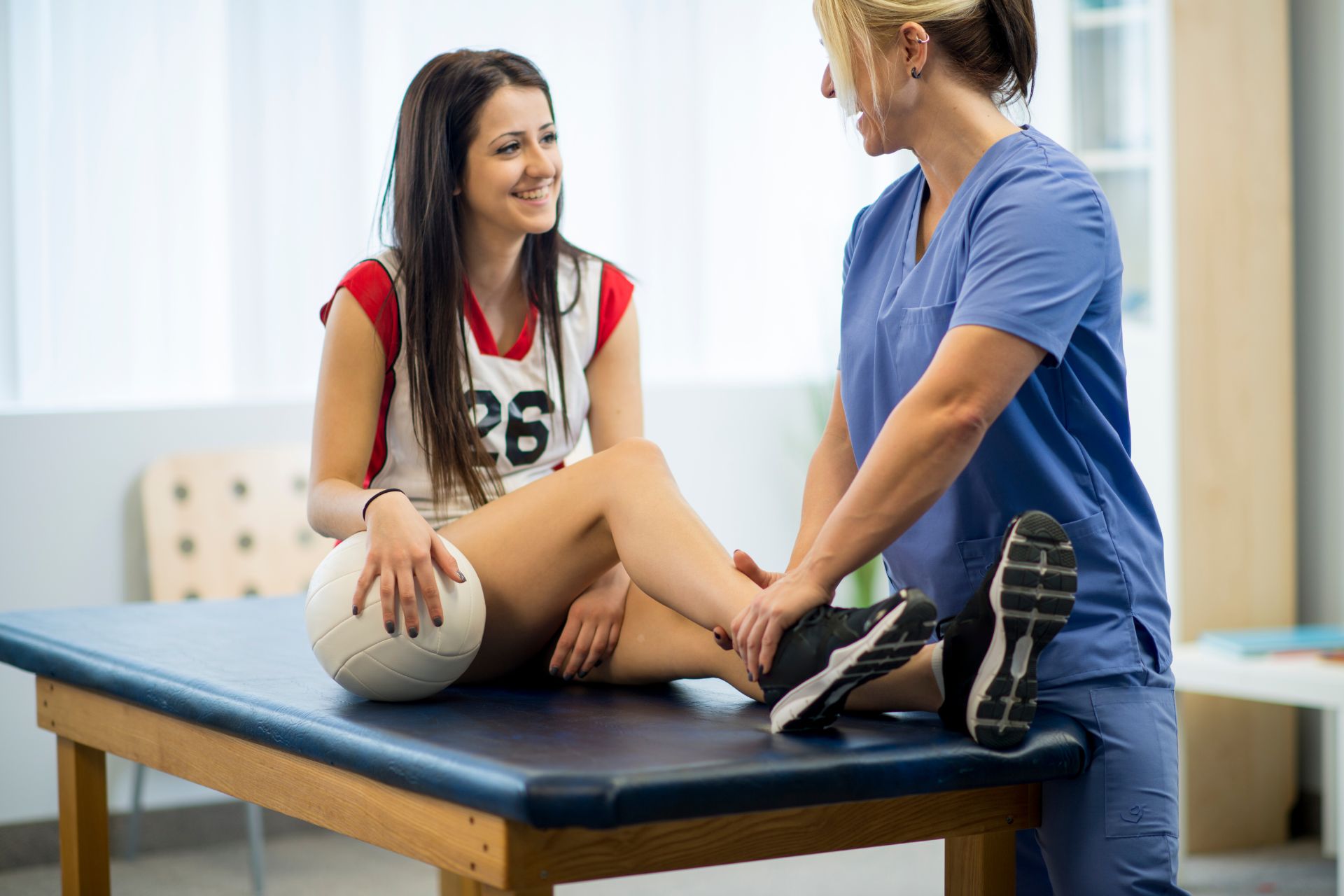
For athletes recovering from an ACL injury, a comprehensive rehabilitation program incorporating specific physical therapy techniques is crucial for optimal recovery and return to sport. Neuromuscular training, which focuses on improving proprioception and dynamic stability, is essential for restoring joint function and preventing re-injury. Plyometric exercises, such as box jumps and agility drills, help in regaining explosive power and coordination. Strengthening exercises targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings, and gluteal muscles are vital for restoring muscle balance and knee stability. Eccentric training, particularly for the hamstrings, aids in enhancing muscle control and reducing strain on the ACL graft. Incorporating balance and core stability exercises, such as single-leg stands and planks, further supports joint stabilization. Additionally, sports-specific drills tailored to the athlete's discipline ensure a smooth transition back to competitive performance. Regular assessment and progression of these exercises, guided by a physical therapist, are key to a successful recovery.
Physical therapy addresses shoulder impingement syndrome in baseball players by employing a comprehensive approach that focuses on restoring optimal shoulder biomechanics, enhancing rotator cuff strength, and improving scapular stability. Therapists often begin with a detailed assessment to identify specific deficits in range of motion, muscle imbalances, and postural abnormalities. Treatment protocols typically include targeted exercises such as scapular retraction, external rotation strengthening, and dynamic stabilization drills to reinforce the rotator cuff and scapular muscles. Additionally, manual therapy techniques like joint mobilizations and soft tissue massage are utilized to alleviate pain and improve flexibility in the shoulder joint. Emphasis is also placed on correcting throwing mechanics and incorporating sport-specific drills to ensure a safe return to play. By addressing these key areas, physical therapy not only alleviates symptoms of shoulder impingement but also reduces the risk of future injuries in baseball players.
Aquatic therapy plays a pivotal role in the rehabilitation of lower limb sports injuries by leveraging the unique properties of water, such as buoyancy, hydrostatic pressure, and viscosity, to facilitate recovery. The buoyancy provided by water reduces the gravitational load on the lower extremities, allowing athletes to perform exercises with decreased joint stress and pain, which is particularly beneficial for conditions like anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, meniscus injuries, and ankle sprains. Hydrostatic pressure aids in reducing edema and improving circulation, which accelerates the healing process. The resistance offered by water's viscosity enables the strengthening of muscles through low-impact exercises, enhancing muscle endurance and joint stability without the risk of further injury. Additionally, the thermal properties of water can help in relaxing muscles and increasing flexibility, which is crucial for restoring range of motion in injured limbs. Overall, aquatic therapy provides a controlled environment that supports early mobilization, promotes neuromuscular re-education, and enhances proprioception, making it an integral component of comprehensive rehabilitation programs for athletes recovering from lower limb injuries.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in preventing re-injury in athletes recovering from hamstring strains by focusing on a comprehensive rehabilitation program that includes strength training, flexibility exercises, and neuromuscular re-education. By incorporating eccentric strengthening exercises, physical therapists can enhance the tensile strength of the hamstring muscles, reducing the risk of future strains. Additionally, dynamic stretching and proprioceptive training improve muscle elasticity and joint stability, which are essential for optimal athletic performance. Therapists also employ gait analysis and biomechanical assessments to identify and correct any movement patterns that may predispose the athlete to re-injury. Furthermore, sport-specific drills and functional training are integrated to ensure a safe return to play, while education on proper warm-up techniques and load management helps athletes maintain muscle health and prevent overuse injuries. Through this multifaceted approach, physical therapy not only aids in the recovery process but also fortifies the athlete's resilience against potential hamstring re-injuries.
Proprioceptive training offers numerous benefits in the physical therapy regimen for ankle sprain recovery, enhancing both functional stability and neuromuscular control. By focusing on proprioception, or the body's ability to sense its position in space, this type of training helps improve joint position sense, which is crucial for preventing recurrent injuries. Incorporating balance exercises, such as single-leg stands and wobble board activities, proprioceptive training targets the mechanoreceptors in the ankle joint, thereby enhancing the sensory feedback loop between the central nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. This leads to improved coordination, agility, and dynamic stability, which are essential for restoring normal gait patterns and athletic performance. Additionally, proprioceptive exercises can reduce the risk of chronic ankle instability by strengthening the peroneal muscles and other stabilizing structures around the ankle, ultimately facilitating a more comprehensive and resilient recovery process.